When attempting to make your website multilingual, you might stumble upon different terms for converting it from one language to another. Maybe you are wondering if you should use transcreation vs translation vs localization to do so but aren’t even sure what the difference between those terms is.
Which one should you apply to your website? Does it matter? Do you have to pick one over the other?
As it turns out, all three have a place in offering your site up in your target language(s) and are important in different contexts. However, to use them correctly, you need to know what they are and when each one is appropriate.
To help you with this confusion, in this post, we will do a deep dive into the topic of transcreation vs translation vs localization for websites. We will give you a definition of each term and examples of their differences. After that, we will show you how you can apply these processes to your WordPress site using a multilingual plugin like TranslatePress.
What Is Translation?
In order to get on the same page about the topic of this post, let’s first settle on some definitions. Because while transcreation, translation, and localization are not the same, they are definitely related and have considerable overlap.
We are starting off with translation since that’s probably what you are most familiar with. It is the process of converting text from one language (the source language) to another (target language) while preserving the original meaning, style, and intent.

The main focus here is accuracy. Whether you are using human translation or machine translation, the primary goal is to faithfully convey the content from the source language in the target language. Translators try to ensure clarity, coherence, and adherence to the original text.
Most Common Usage
Considering the above definition, it’s probably not surprising that translation most often comes into play for forms of written text where the literal transfer of information is important. Examples include technical documents, emails, legal texts, scientific papers, directions for use of medication, literature, and more.
When it comes to websites, translation most often applies to blog posts, technical tutorials, menus, and other fact-based elements. Anything that is central to website navigation and where you need to ensure that the meaning is clear to visitors.
Translation Examples
Look at the content of this website footer belonging to a well-known clothes brand:
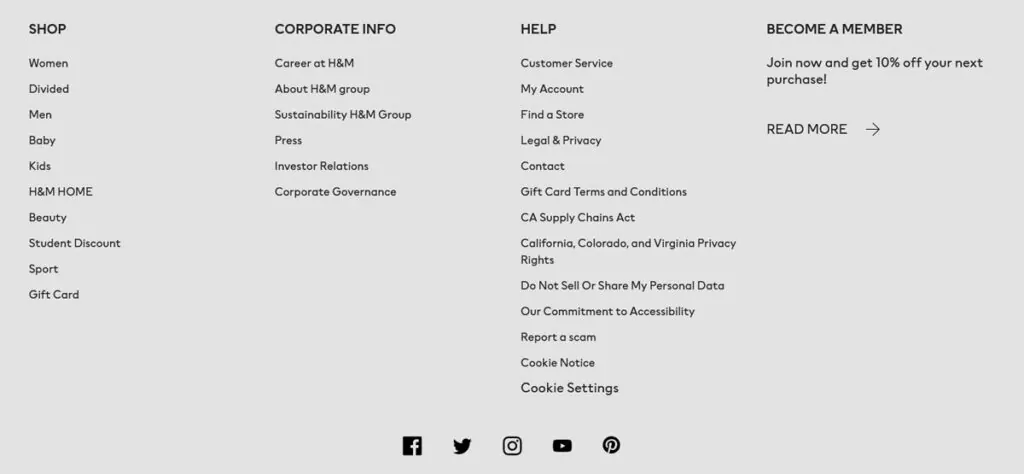
As you can see, these links pretty much only have informational value. They lead you around the site and give you more information about what content to expect from it. They don’t need a lot of work in terms of creativity or adjustment to a certain group or locality. Therefore, a simple transfer from one language to another is enough.
What Is Transcreation?
Transcreation, on the other hand, is less concerned with the literal accuracy of the translation. Made up of “translation” and “creation”, it is less about adapting a text from one language to another. Instead, transcreation is about maintaining the intended message, tone, and emotional impact of the content.
As such it tries to recreate those parts so that the content resonates with the target audience in the same way but in a different context. To do that, transcreation often requires creative liberties, such as modifying cultural references, idiomatic expressions, and even rewriting portions of the text. For that reason, it often starts with a creative brief rather than text to translate and uses copywriters, not (just) translators.
Areas of Application
Transcreation commonly comes into play for marketing materials like advertising campaigns, slogans, and taglines. It’s often necessary when trying to adapt the image of a global company to a local market. Transcreation helps to recreate the brand message and keep its intention but not necessarily the same words.
This also applies to websites. Here, to adapt your marketing elements like banners or calls-to-action, it’s much more important to get the message right than to provide a word-for-word equivalent.
Besides that, transcreation also applies to poetry and other creative content where cultural adaptation and emotional resonance are crucial.
Examples of Transcreation
A frequent use of transcreation is the adaptation of company names between completely different alphabets. A good example here are international companies who try to enter the Chinese market.
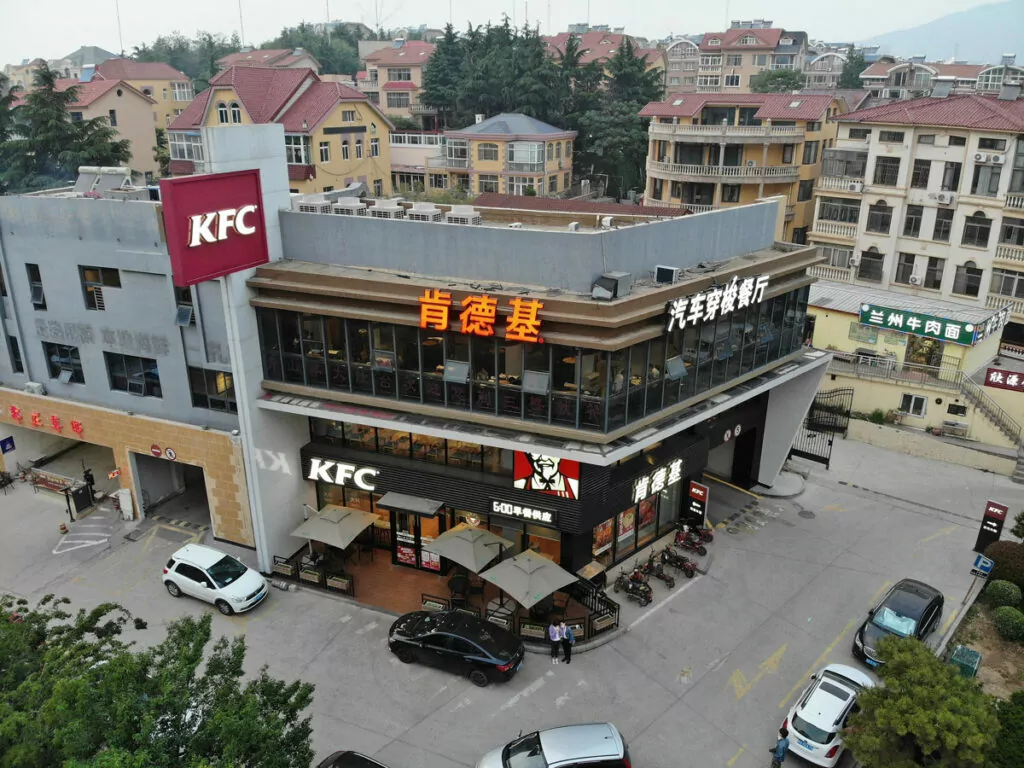

Chinese doesn’t use the Roman alphabet and also has a very different sound inventory than, say, English. Therefore, to “translate” brand names, a common practice is to choose characters that imitate the sound of the company name and also have related or at least positive meaning. Here are some examples:
- KFC — Written 肯德基 and pronounced kěndéjī in Chinese. The characters mean “to be willing/agree/be ready”, “virtue”, and “base” or “foundation”. The name doesn’t really mean anything by itself but sounds similar and is full of positive connotations.
- Mercedes Benz — Mercedes settled on 奔驰 as its Chinese name, which is pronounced bēnchí. Again, it’s a very similar sound and also has a meaning that makes sense, which is “to run quickly” or “to speed”.
- BMW — This car marker’s name in China is 宝马. It is pronounced bǎomǎ and means “precious horse”. Makes a lot of sense for a luxury car, don’t you agree? Fun fact: colloquially in China, “BMW” also stands for “bié mō wǒ”, which means “don’t touch me”.
The above examples are a good way to understand the difference of translation vs transcreation. As you can see, none of the company names have actually been translated but merely adapted in spirit.
What Is Localization?
Finally, localization means adapting a product, service, content, or website to a specific locale or target market. For that, you need to not only translate the words but consider linguistic, cultural, technical, and even regulatory aspects. It’s an overall adjustment to the target market and audience not just in terms of language but also taste and tone.
For example, localization looks different whether you are targeting customers in Argentina, Mexico, or Colombia – even though these countries all speak Spanish. However, their versions of Spanish use different slang, idioms, and even words. For example, Mexicans use the standard “tú” for the second person singular pronoun (“you”), while in Argentina they say “vos” instead.
What’s more, if you were to localize your website for Spain, you would also likely have to translate it to Catalan, which is a language spoken by several million people in that country. Besides other dialects. That, too, is part of localization.
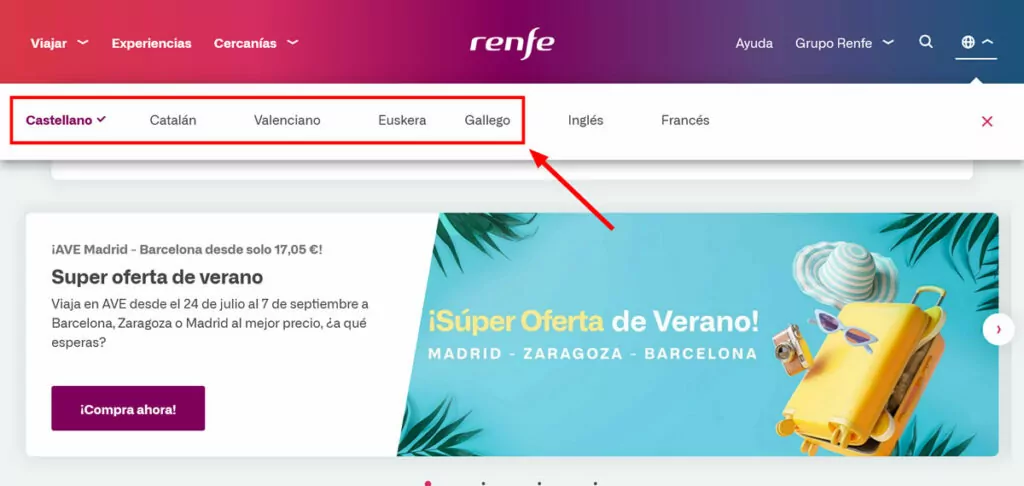
Because of this added complexity, localization can often include both translation as well as transcreation.
Localization is commonly used in software and website localization, video game adaptation, product packaging, and for user interfaces.
Localization in Detail
Here are just a few things that fall under the umbrella of localization:
- Spelling — Different English-speaking countries have adopted more than one spelling for certain words. See “localization” vs “localisation” or “color” vs “colour”.
- Cultural references — Even if two locales speak the same language on paper, they can still call things by different names. What Americans call “elevator”, their British counterparts would refer to as “lift”. “Pants” vs “trousers” is another common example. It’s important to get nuances like this right to avoid confusion and also properly address your target market.
- Units of measurement — Depending on what market you are targeting, you would either speak about miles and feet or kilometers and meters, A4 vs letter-sized paper, or kilograms vs pounds. Not to mention the myriad of global currencies. This especially important for localizing online stores.
- Date formats — How to denote the date of the day varies across the world. For example, 04/02/2011 would be April 2nd in the US but February 4th in many other countries. On the other hand, many European countries don’t use slashes at all and would instead write the same date as 04.02.2011.
There is more that goes into properly localizing your content. When you do it right, you don’t just speak to your audience’s minds but also their hearts.
Localization for Websites
Besides the more general points of localization mentioned above, there are special considerations for websites. Since they consist of more than textual content, there are other things to keep in mind.
- Layout — Some languages tend to be more verbose than others and translating them can result in longer or shorter text. Some languages run from right to left. All of that has influence on your website spacing and can influence layout and design.
- Colors — Colors have diverse meanings across cultures. While black is the color of mourning in much of the Western world, in many places in Asia its actually white. Plus, in some countries in Africa, it’s red. This is important to know in order to localize things your website design properly so that it has the message you intend.
- Visuals — It’s important to consider the cultural backgrounds in images and videos you use. For example, as a beer company in Europe you might show people enjoying your product while watching soccer, while in other areas you would have to use other sports that are more popular locally. The nationality of people appearing in your visuals might also change to help visitors better identify with them.
- Legal requirements — By now, websites operating in the European Union need to have cookie banners in order to conform to privacy laws. Ensuring you adhere to local laws is a crucial part of localization to avoid fines and lawsuits.
- SEO — Search engine optimization relies a lot on textual cues in certain locations that decide where and for what target keywords your website will rank. Think back to the elevator/lift situation. If you are a company selling elevators (or lifts) and want to target different locales, you would need two optimize two different pages to do so.
TranslatePress Multilingual
TranslatePress is the easiest way to translate your WordPress site. It's fast, won't slow down your website, works with ANY theme or plugin and it's SEO friendly.
Get the pluginExamples
Localization is most visible when you compare the websites of multinational companies in different localities. For example, here is the US site of a popular fast-food chain.

Pretty straightforward. It’s all about convenience and getting your food as quickly as possible. Now compare that to its Japanese counterpart.
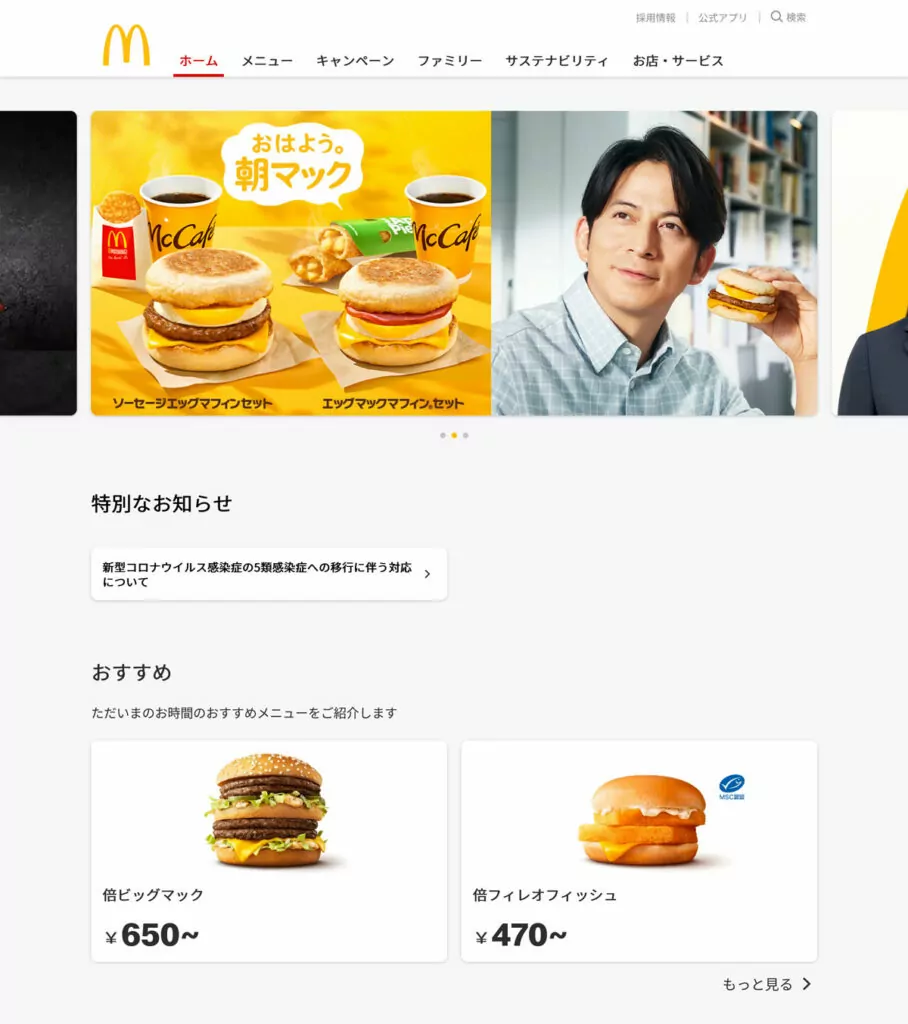
Looks a bit more high end, doesn’t it? The site is also advertising different products and the content and design of the homepage is not the same. Besides, of course, being in Japanese.
How TranslatePress Can Help You
As you can see from the above, when comparing translation vs transcreation and localization, each of them involve a lot of effort in and by themselves. If you want to apply them to your website, it helps if you have a tool that makes their implementation on your website as easy as possible. Here’s how TranslatePress can be this tool for you.
Easy to Use
In TranslatePress, pretty much all translation happens in one simple-to-use interface.
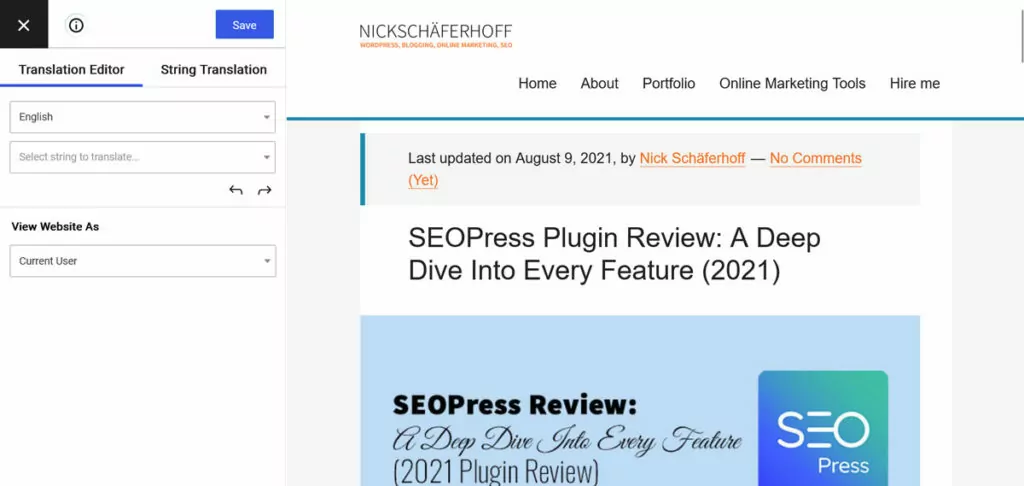
You simply pick the content you want to convert from a drop-down list, via two arrow buttons, or by picking it from the preview screen.
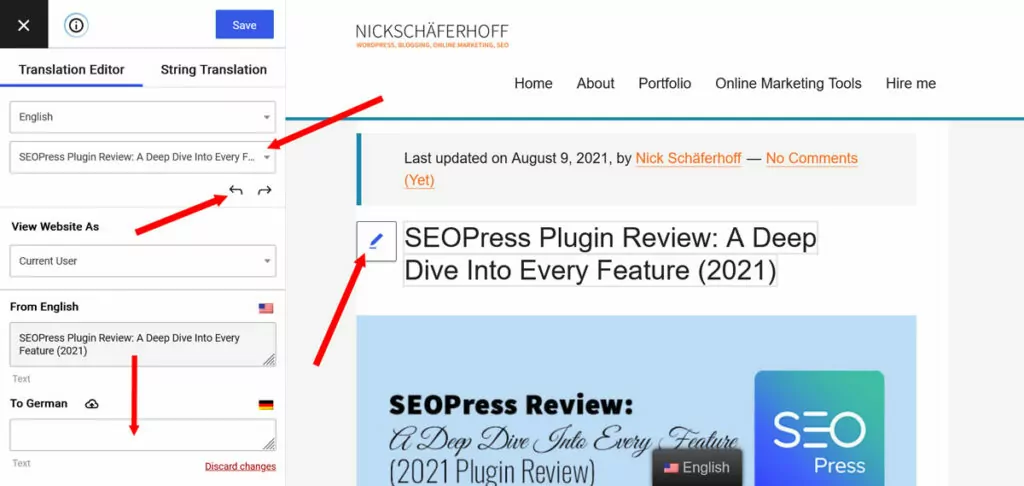
Then, you can simply enter the translation, save, and visitors will automatically see the new version. That’s it!
This simplicity allows you to fully concentrate on what really matters: getting the translation and localization of your website right, not how to do it.
Works for All Your Content
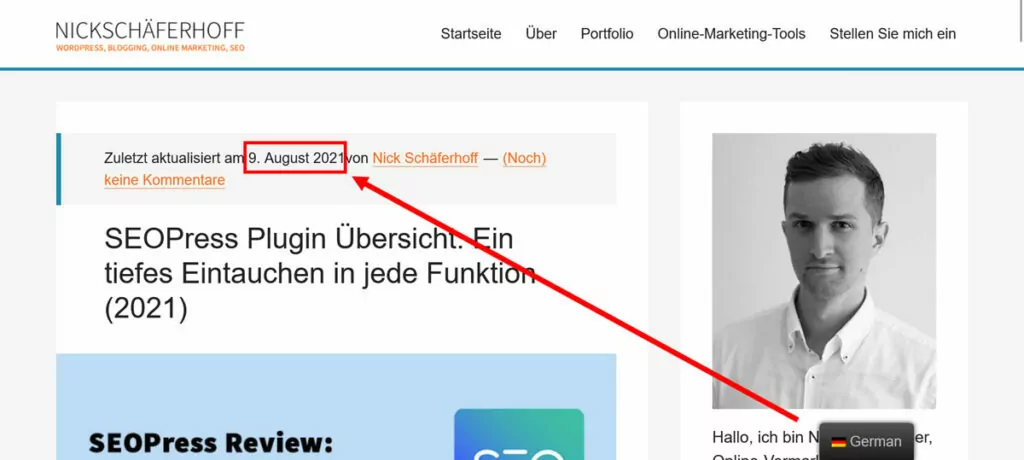
The plugin works with virtually all types of WordPress content: posts and pages, custom fields, custom post types, shortcode output, menus, forms, and more. It even automatically localizes date and time formats to your target language.
In addition, there is a separate menu to translate strings from your themes and plugins.
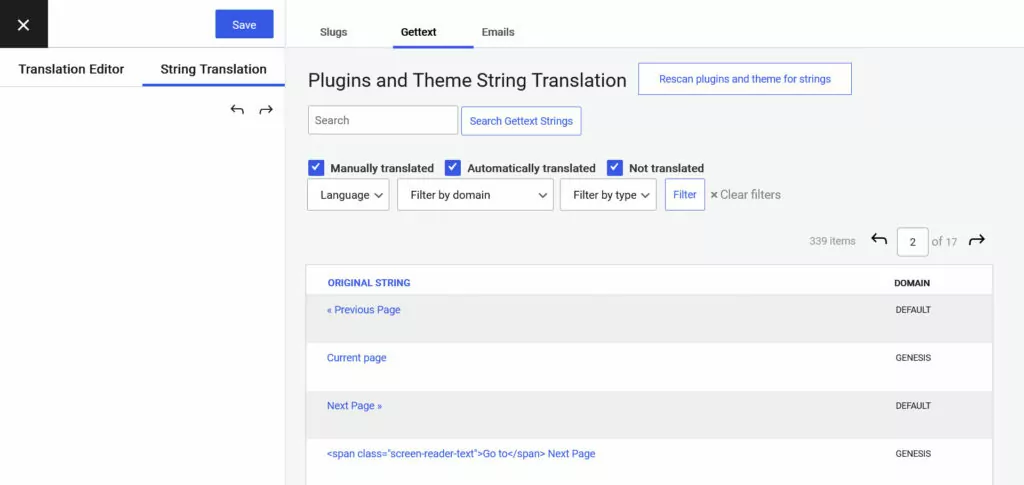
TranslatePress automatically scans the components of your site and provides a list of strings coming from them so you can input other language alternatives.
Create Different Locales, Not Just Languages
Above, we have talked about how localization not only means translating your site into different languages but adapting them to different locales, even if they speak the same language on paper. TranslatePress can also help you with that.
Under TranslatePress → Settings, you can set up as many different locales as you want. In fact, TranslatePress comes with many of them out of the box, such as American, British, Canadian, or Australian English, different version of German (Germany, Switzerland, Austria), or Spanish (Spain, Mexico, Peru, Chile, and more).
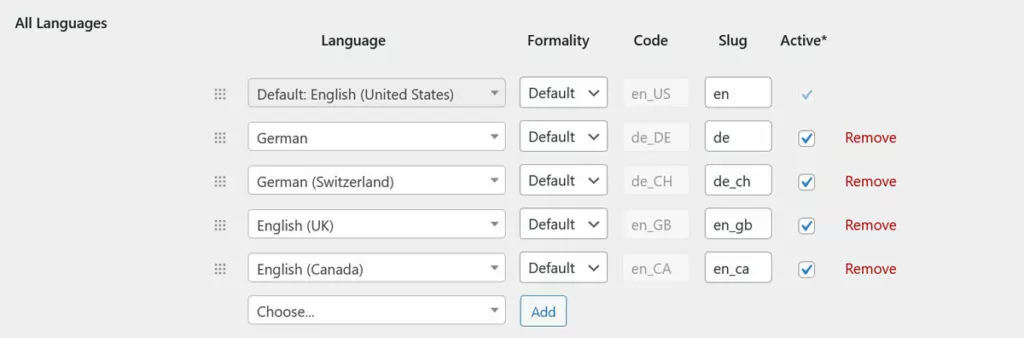
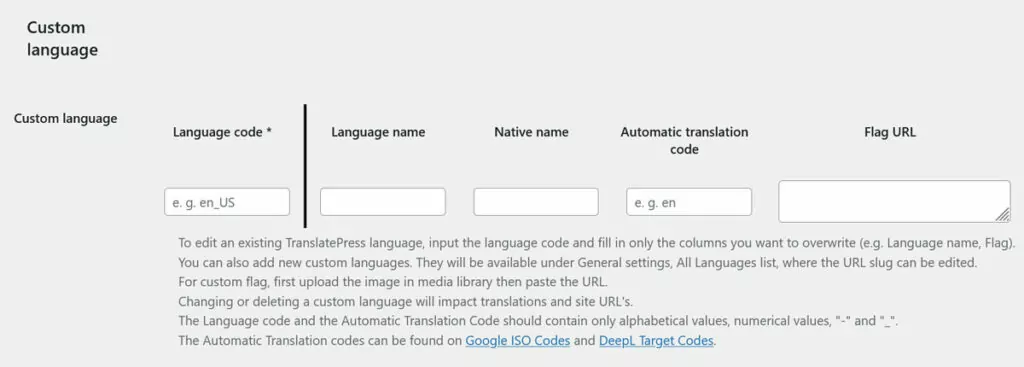
If that isn’t enough, you still have the option to create custom languages and locales under the advanced options.
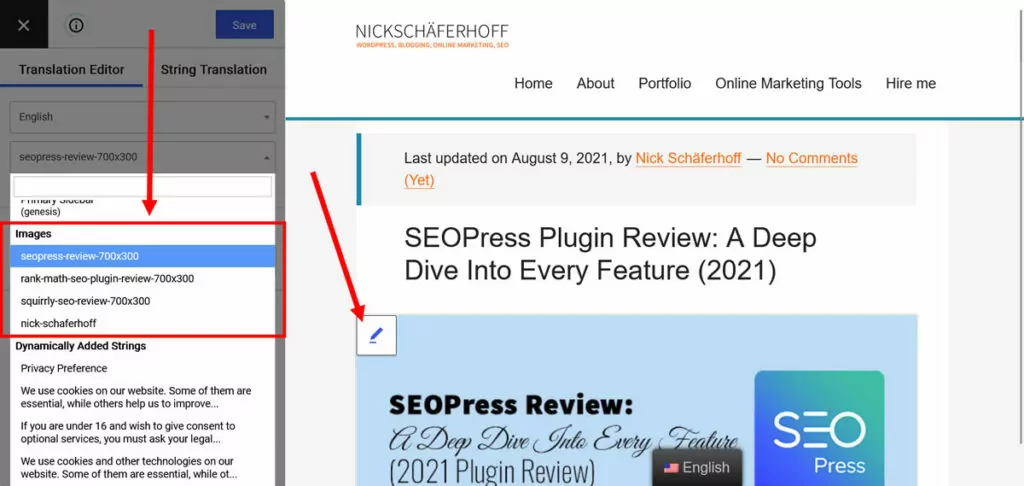
Localize Images
Earlier we stressed the importance of not only translating your text but also localizing your images. In the same place where you adjust your written content, you can also provide visuals in different languages. Simply pick an image from the drop-down menu under Images or from the preview window.
When you do, TranslatePress gives you the option offer up an alternative.
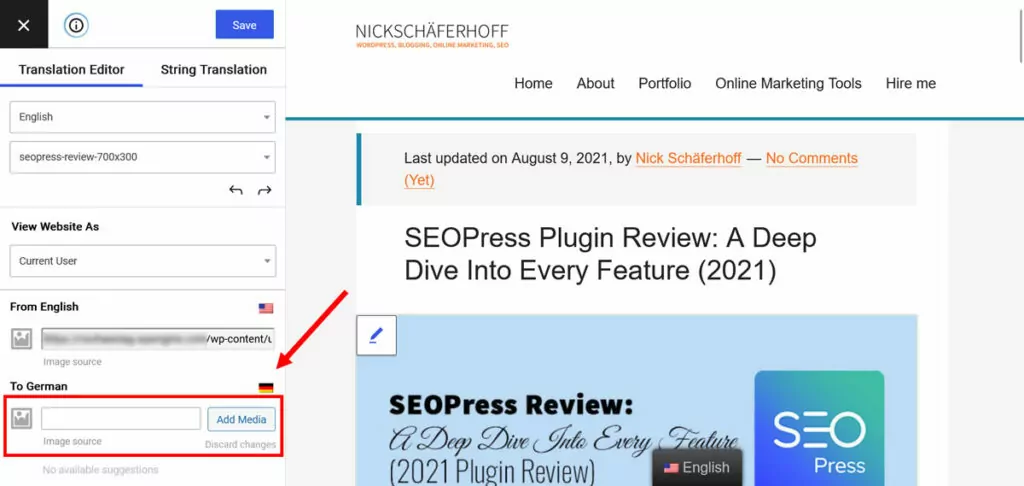
Pick one, save, and it will appear on the translated version of your site.
Multilingual SEO
Localization is not just about translation, you also need to internationalize your website structure for search engines if you hope to rank well for your target markets. You can use the SEO pack add-on to adjust URL slugs and provide localized URLs.
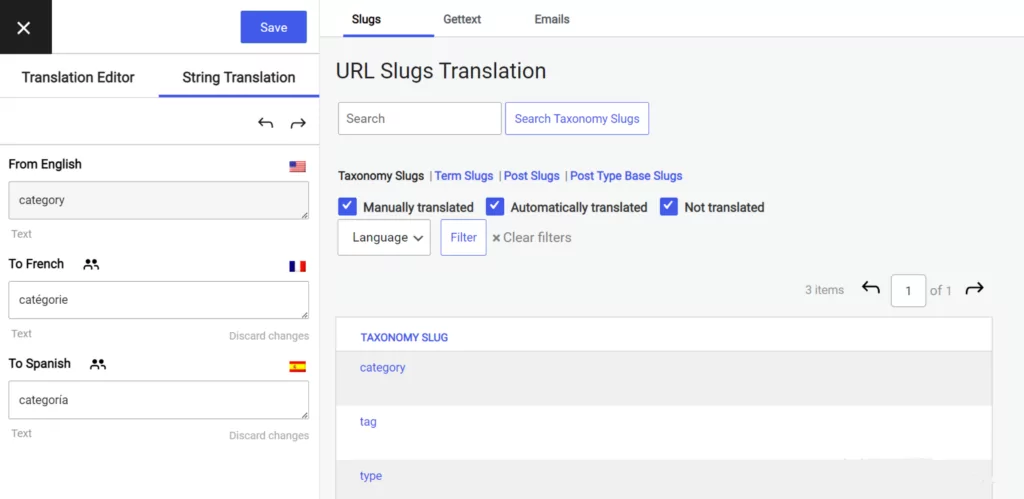
It also works out of the box with common SEO plugins like Yoast SEO. Plus, you get language detection to redirect visitors to their preferred language version automatically.
Machine Translation
As discussed in this post, translation is the basis for website localization. To give you a leg up and do a lot of the heavy lifting for you, you can connect TranslatePress with machine translation services by Google and DeepL.
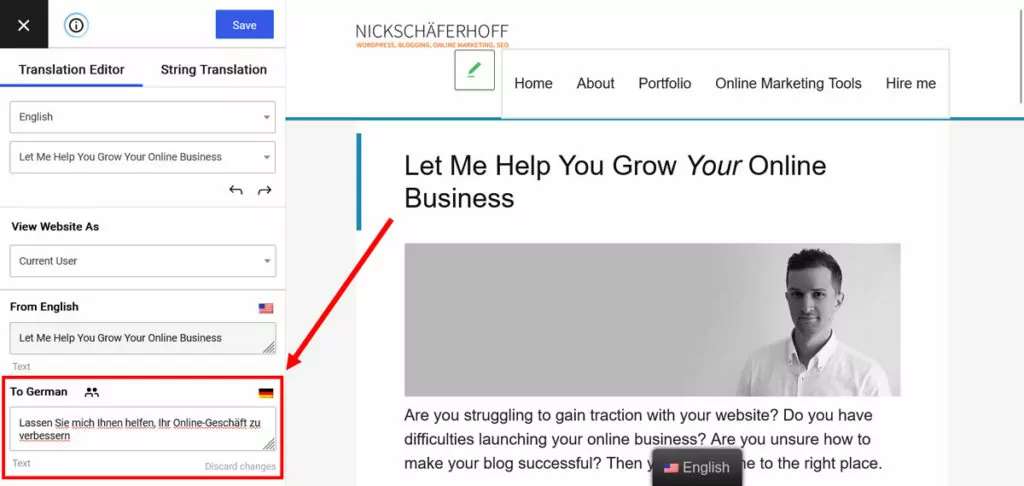
Once in place, the plugin automatically proposes machine translations in its interface that you can use as basis for your localization and transcreation efforts.
Transcreation vs Translation vs Localization: Do What’s Right for Your WordPress Website
Making your website multilingual involves many different processes to make it attractive for your target audience. In this article, we have discussed three of them.
While translation is about faithfully converting text from one language to another, transcreation is about transferring ideas, marketing messages, and feelings without necessarily using the same words. Localization, on the other hand, means adjusting your content and website fully to a target market, complete with language, visuals, units of measurements, and everything else that’s part of language identity.
The truth is, when opening up your web presence to a new language audience, you most likely will use all three of them. For that reason, it’s important to understand what translation means vs transcreation and localization. That way, you can make good use of them.
After that, the only thing that’s left is to choose the right tool for translating/transcreating/localizing your WordPress website. Hopefully, we have been able to show you that TranslatePress is a plugin you can rely on for that.
TranslatePress Multilingual
TranslatePress is the easiest way to translate your WordPress site. It's fast, won't slow down your website, works with ANY theme or plugin and it's SEO friendly.
Get the pluginWhat do you use most to make your site multilingual – translation, transcreation, or localization? Share your experience in the comments!


