Elevating your business to multi-national status is not magic. By localizing and translating your website, you can easily communicate with potential global clients about your products and services. But it’s not enough to translate and localize your website. Your efforts will only yield meaningful results when you go a step further to implement multilingual SEO.
In this article, we’ll focus on what multilingual SEO is and why you need it for your website. We’ll also show you the step-by-step process of optimizing your website content using our multilingual SEO plugin called TranslatePress.
TranslatePress Multilingual
TranslatePress is the easiest way to translate your WordPress site. It's fast, won't slow down your website, works with ANY theme or plugin and it's SEO friendly.
Get the pluginTable of Contents
- What Is Multilingual SEO?
- 5 Benefits of Multilingual SEO
- Multilingual SEO Best Practices (7 Steps and Tips)
- Multilingual SEO FAQs
What Is Multilingual SEO?
Multilingual SEO is the process of optimizing your website for different languages. The goal is to ensure that multiple audiences who speak different languages can easily access your site’s content from anywhere in the world using organic search.
Multilingual SEO enables you to create content in multiple languages and ensure that such content reaches the right people.
While the most popular language on the Internet is American English, only a small percentage of netizens identify it as their first language. This means you have to divest your SEO efforts beyond the English language if you want your business to enjoy global success.
Relying on automated translations like Google Translate may be an easy option when translating Google search results. But if you desire the best results, using a multilingual website SEO strategy is important.
5 Benefits of Multilingual SEO
Your business has much to gain when incorporating multilingual SEO into your website. Check out these five amazing benefits of multilingual SEO.
1. You Get Ahead of Your Competitors. In the past, some countries, like the United States and the United Kingdom, were the concentrated centers of online businesses. But today, other countries, like Japan and China, have also harnessed the virtual space for business transactions.
These users come from different language groups worldwide. With multilingual SEO, you can outdo your major competitors in your industry. Since SEO for multilingual websites helps you access and communicate with a global audience, you can drive traffic to your website worldwide.
2. You Boost Your Site’s Overall SEO Ranking. Having translated versions of your site can improve your chances of appearing on the first page of search engines. A multi-language website can drive more traffic than a single-language site. Search engines will identify all translated versions as embedded in one site. Searches on all these versions of the website site drive traffic to the main website and create a positive compound SEO ranking effect.
3. You Reach a More Specific Target Audience. SEO for a multi-language website goes beyond merely translating your website into multiple languages. The process involves determining the specific group of people you intend to reach and translating your website into their native languages. Geo-targeting is handy in providing a platform for a more targeted reach in specific locations.
4. Continued Business Growth. A multilingual website also allows you to maintain a consistent structure of creating awareness about your brand and keeping your global audience informed about your products and services. You’ll be able to drive more traffic to your website and make returns on your investment now and in the long term.
5. Access to More Search Engines. Countries like China and Japan have major search engines different from the popular ones like Google and Bing. Search engines lead people to your website, and having access to many other local alternatives means more traffic. A multilingual website is the only channel through which you can achieve this.

Multilingual SEO Best Practices (7 Steps and Tips)
Now that you know how beneficial multilingual SEO is to your business and website, let’s take a look at some tips on how to do multilingual SEO effectively.
1. Choose the Right URL Structure
There are four main approaches to structuring URLs for multilingual sites:
- Subfolders
- Subdomains
- Separate domains
- URL parameters.
Each option has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, impacting SEO, user experience, and site maintenance differently.
Subfolders (or Subdirectories)
Subfolders add a specific language or country code directly after the domain name in the URL (e.g., example.com/en/ for English or example.com/fr/ for French).
Pros:
- Consolidated Domain Authority: All language versions contribute to the same domain authority, potentially improving overall site ranking.
- Simpler Setup and Maintenance: Easier to manage than separate domains or subdomains, as everything resides under a single domain.
- User-Friendly: Clear and logical URL structure for users, indicating the language or regional focus directly in the URL.
Cons:
- Potential for Content Duplication: Search engines might see similar content across subfolders as duplicate content without proper hreflang tags.
- Limited Geo-Targeting Flexibility: While it’s good for language targeting, it’s less flexible for geo-targeting specific countries.
Subdomains
Subdomains place the language or country code as a prefix to the main domain (e.g., en.example.com for English, fr.example.com for French).
Pros:
- Geo-Targeting: Offers better geo-targeting capabilities by allowing search engines to treat each subdomain as a separate entity.
- Flexibility: More flexible in content and design customization for different languages or regions.
- Resource Allocation: Allows for the distribution of server resources, improving site speed for localized versions.
Cons:
- Split Domain Authority: Each subdomain is treated as a separate domain, which might dilute domain authority and require more effort in link building for each language.
- Complex Setup and Maintenance: More complex to set up and manage than subfolders, especially for SSL certificates and hosting configurations.
Separate Domains
This approach uses completely different domains for each language or country version of the site (e.g., example.fr for France, example.de for Germany).
Pros:
- Maximum Geo-Targeting: Offers the highest level of geo-targeting and local signaling to search engines and users.
- Cultural Customization: Allows for extensive customization to cater to cultural differences and preferences in each market.
- Clear Local Presence: Signals a strong local presence, potentially increasing trust and relevance in the target market.
Cons:
- High Costs and Maintenance: Requires purchasing and maintaining multiple domains, along with separate SEO strategies and link-building efforts.
- Divided Domain Authority: Each domain starts from scratch with domain authority, requiring more effort to establish credibility and rank well.
URL Parameters
URL parameters add language or country information as query strings to the URL (e.g., example.com/?lang=en).
Pros:
- Simple to Implement: Easy to add to existing URLs without significant changes to the site’s structure.
- Flexibility: Can be used dynamically to switch between languages without creating separate pages.
Cons:
- SEO Unfriendly: Generally not recommended for SEO as search engines may struggle to crawl and index content correctly.
- User-Unfriendly: Creates cluttered and less intuitive URLs for users, potentially impacting the user experience.
The choice of URL structure for a multilingual website depends on various factors, including the target audience’s geographic locations, the website’s size and complexity, and available resources for SEO and maintenance.
Subfolders are often recommended for their simplicity and consolidated domain authority, but the best choice varies based on specific business needs and goals.
2. Start With Quality Keyword Research
To kick things off, it’s important to do comprehensive keyword research before translating your website content. This is because different segments of your global audience have varying interests—in other words, different search intent.
For example, let’s consider the keywords ‘content creation’ in English and ‘creation de contenu’ in French.
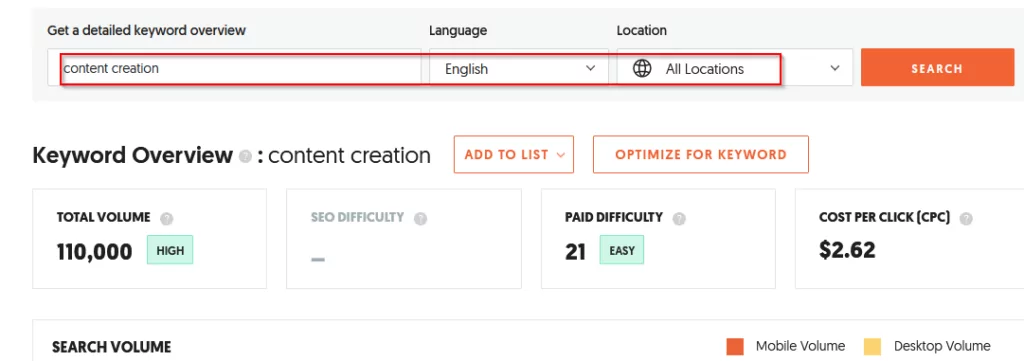
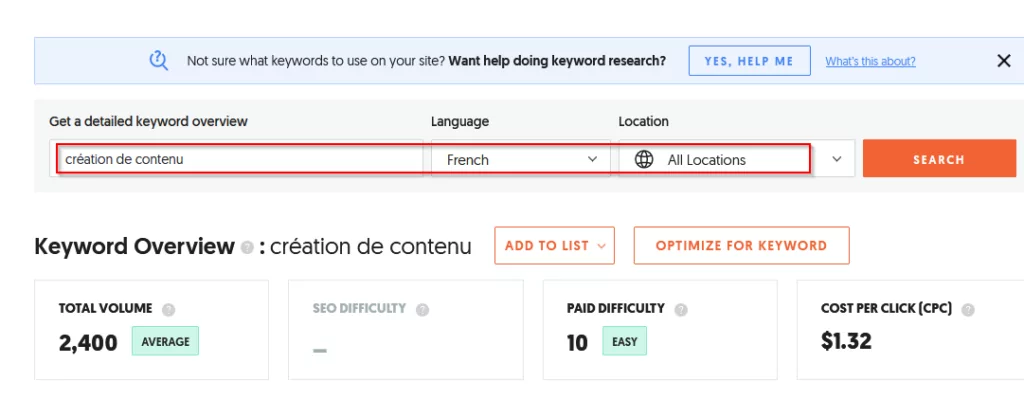
The French translation obviously has a significantly lower search volume than the English version.
Quality keyword research helps you put your translation and localization efforts into perspective. This way, you can analytically determine which keywords to pay more attention to for each translated version of your site.
Ahrefs and Semrush are great tools that can help you find out the search volume of your desired keywords in different languages.
Gaining mastery of the appropriate use of keywords in your language can be tasking. You’ll try to ensure you’re not using keywords that do not help boost your content’s SEO performance. Doing this in multiple languages you don’t understand could be even more daunting.
Notwithstanding, keywords are essential in the translated versions of your website, and you need to pay attention to them when you translate them. The first thing to do is find out the most common English keywords on your website. Ahrefs can help you get started.
Once you have your list, search for the most accurate translations of those keywords in the target translation language(s). TranslatePress can help speed up this process with its automatic translation feature. But you still need to cross-check each page manually because machines cannot guarantee 100% accuracy when it comes to translation. If you happen to find any mistakes, simply go in and do a manual correction.
You can do this very easily from the visual translation interface by simply clicking the pencil icon near a piece of text and inputting its correct translation in the sidebar, like so:

3. Translate Your URL Slugs
When translating your website, it is also important that you pay attention to your URL slugs. Slugs are parts of your URL that follow your domain name. For instance, if the URL for the payments page of your website is mysite.com/payments, a customer searching the French version of your site should see it as mysite.com/paiements. The slugs here are “payments” (English) and “paiements” (French). This is helpful for both search engines and actual human visitors, as it makes it very clear that these are 2 versions of the same page, only in different languages.
But how do you do this? You can use a plugin like TranslatePress. It makes it easy to change URL slugs as you translate each page.
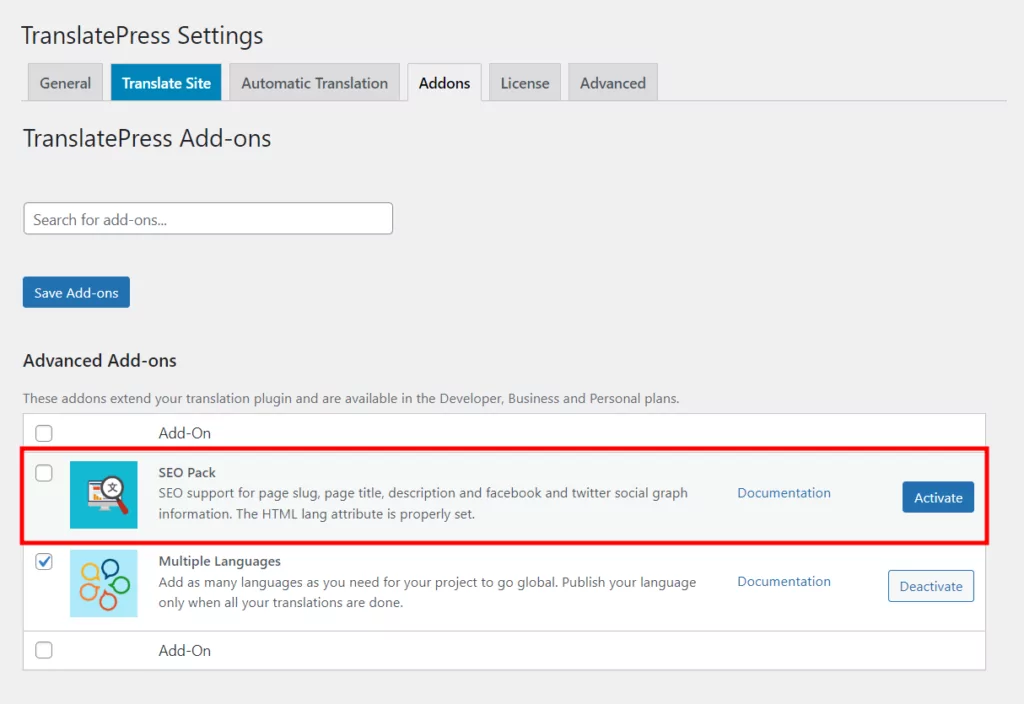
To translate URL slugs with TranslatePress, you’ll need the SEO Pack add-on, available with the premium plans of the plugin. Once you’ve installed the pro plugin and set up at least one new language, the process is as easy as it gets.
Simply navigate to Settings → TranslatePress → Addons tab. Then identify the SEO Pack add-on and click on Activate next to it.
Now you can just go to the front end of your site, click the Translate Page button from the admin dashboard and the translation interface will open up. From the strings dropdown to the left, you can just select the page slug and input its translation below. Don’t forget to hit Save translation when you are done.
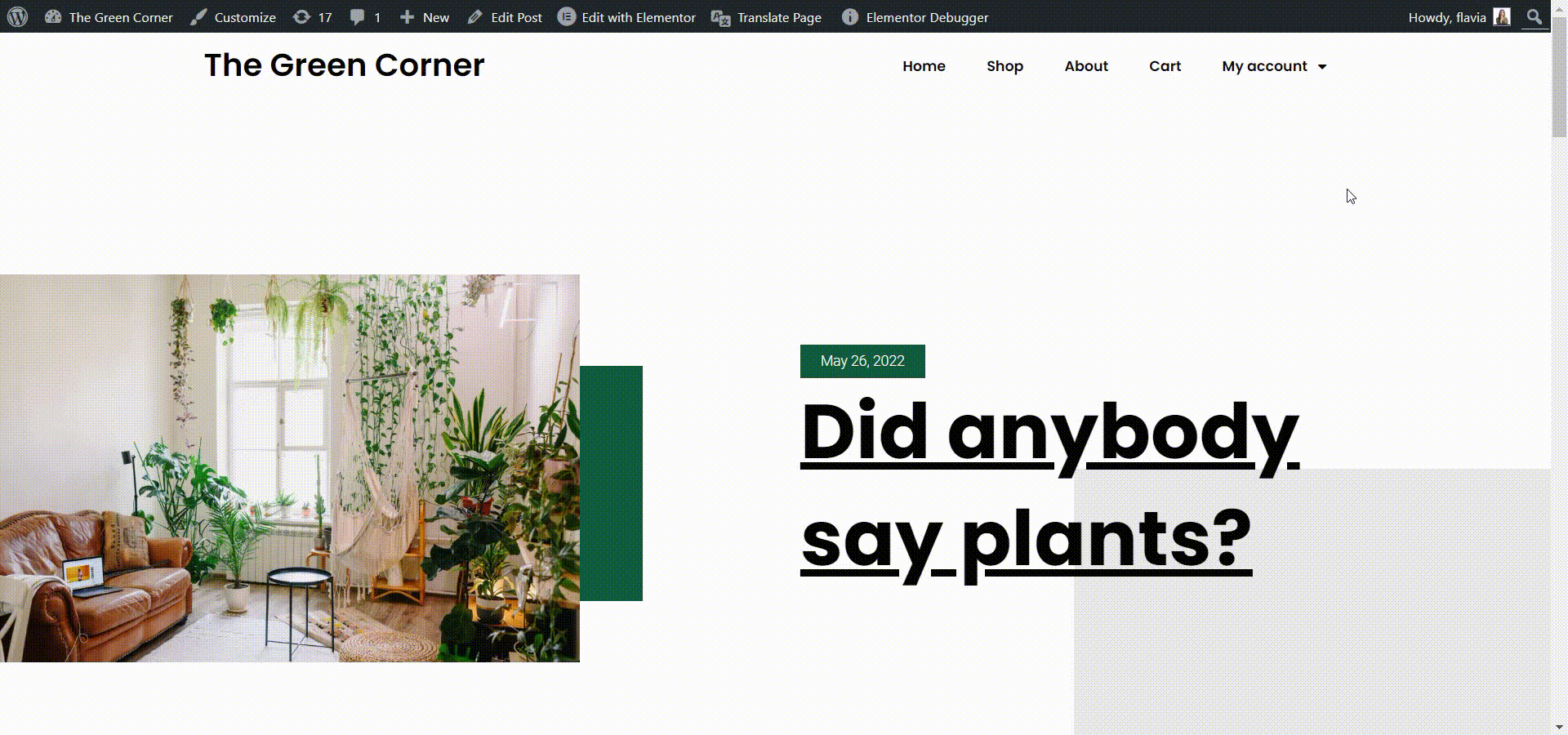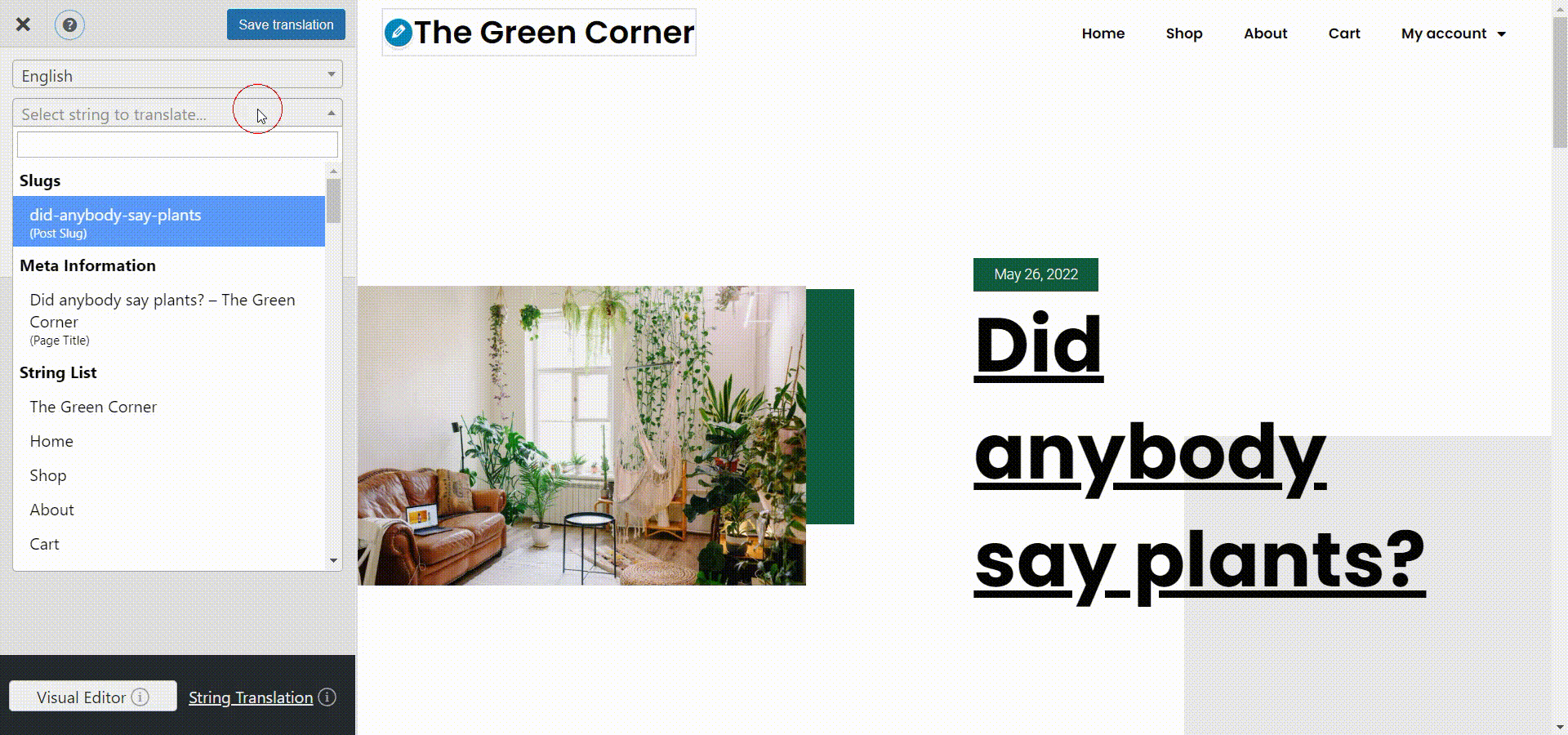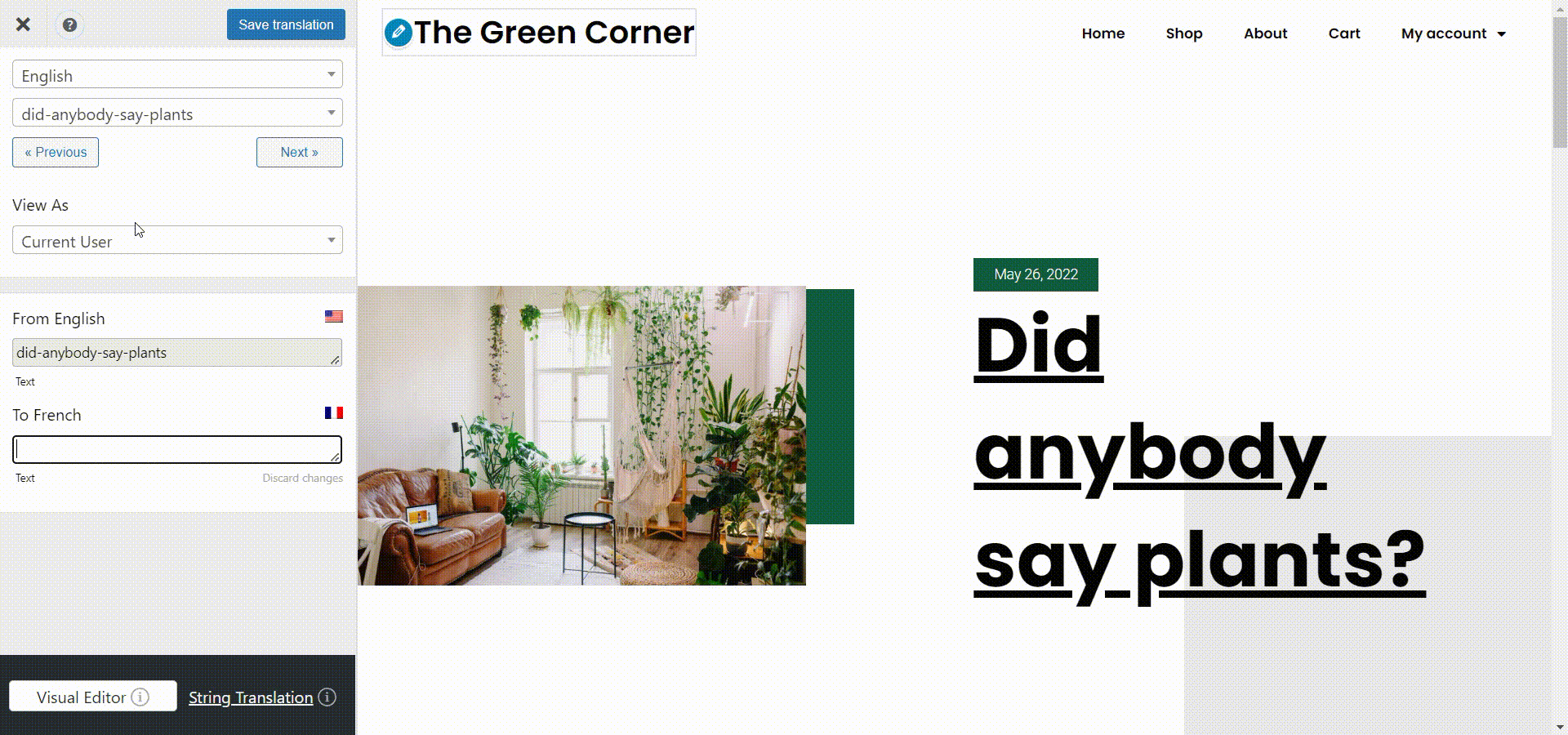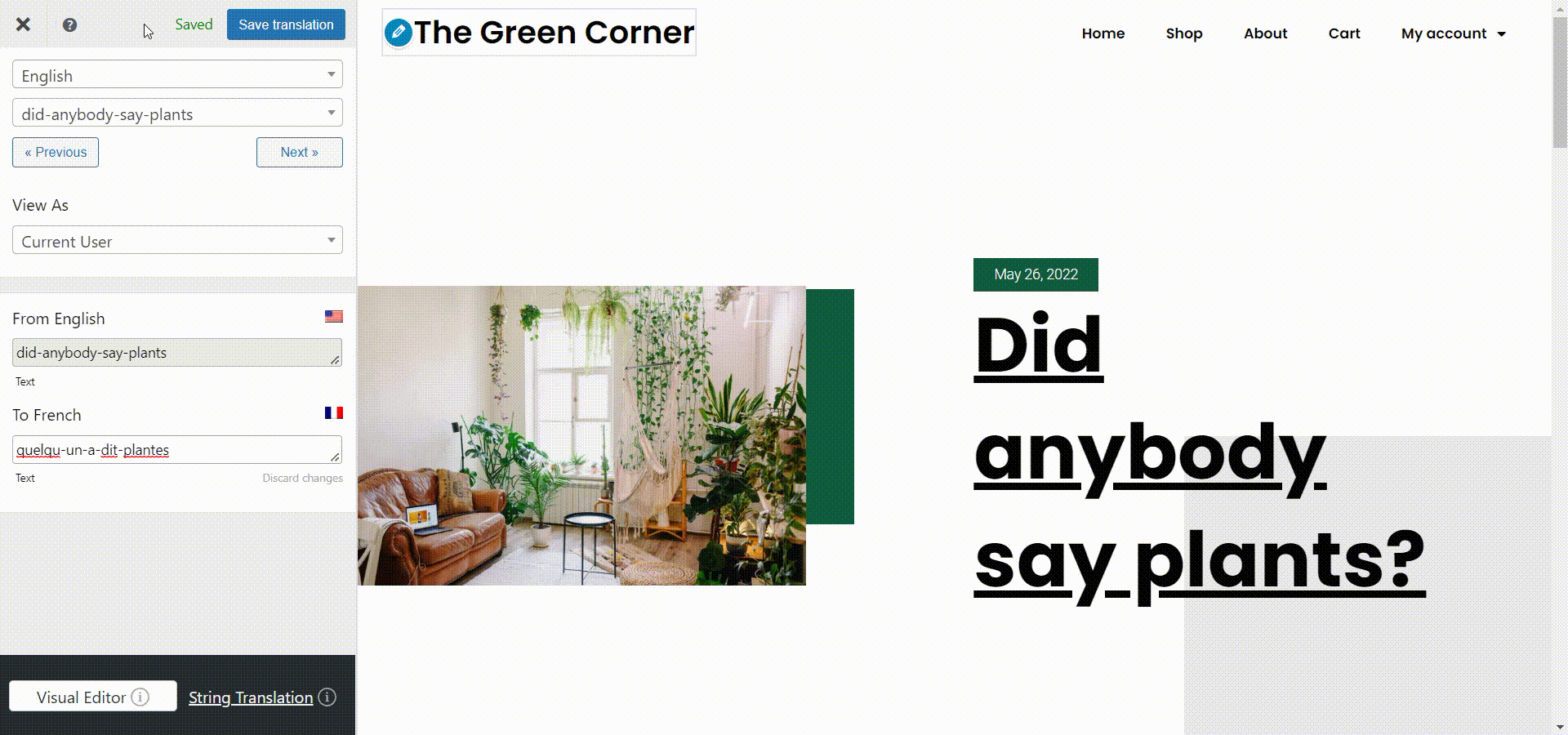
You will find the option to modify the slug just below the language box. Besides this, you’ll be able to translate all the important SEO elements on a page, like the page description, image alt tags, and more.
4. Apply hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags serve as direct signals to search engines, indicating the language and geographical targeting of a webpage’s content.
Hreflang tags are indispensable for sites targeting multiple countries or languages. They ensure that search engines display the appropriate version of content to users. For example, if your site has content in English for the US and the UK, correctly implemented hreflang tags will help distinguish between these versions, catering to the subtle differences in language usage and preferences.
By marking pages as intended for different languages or regions, hreflang tags help avoid duplicate content penalties. Even though the content might be similar or identical across different language versions, hreflang tags signal to search engines that this is intentional and not manipulative duplication.
A hreflang tag is an HTML attribute you include in a webpage’s <head> section. It tells search engines like Google the language (using ISO 639-1 codes) and the page’s geographical target (using ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 codes).
For instance, a French version of a site aimed at users in France would use the hreflang tag: <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”fr-FR” href=”http://example.com/france” />. This tag helps search engines understand that this particular page is designed for French-speaking users in France.
You can apply hreflang tags to your pages manually. But you can also lessen your burden by using TranslatePress. For every language you add, TranslatePress automatically assigns an hreflang tag to every page.
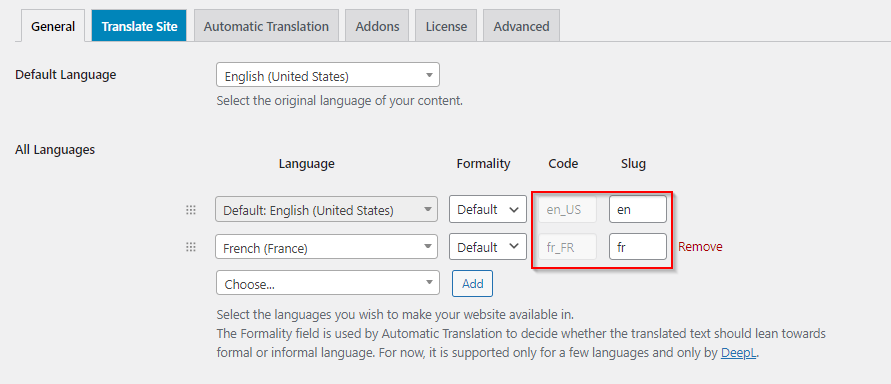
5. Create a Multilingual XML Sitemap
Just like a normal sitemap, the multilingual one helps Google better understand the structure of your website. A multilingual XML sitemap will tell the search engine what language and which locale is used on every single page of the site.
Manually creating such a sitemap, however, can be a daunting task. But we have a better solution.
TranslatePress works seamlessly with the most popular SEO plugins (such as Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or SEOPress) and creates your own multilingual sitemap automatically. You don’t even have to lift a finger once the plugin is installed.
6. Translate Your Site’s Metadata
Finally, there are other components of your website that users cannot see because they are exclusive to search engines. These components are altogether known as metadata. Driving traffic from people who speak other languages than your native language to your website is virtually impossible if you don’t translate your metadata.
To be precise, your site’s metadata primarily consists of both the SEO title and meta description of each page. Other elements include tags, image alt text, etc. For the best multilingual SEO performance, you’ll want to translate each of these elements for every translated page of your site as well. The good news is that TranslatePress helps you achieve this without any hassle.
This is once again possible through the SEO Pack add-on, which lets you translate any meta information. So, go to the page you want to edit while logged into your WordPress admin account. Then click Translate Page at the top of the page. Select the string you want to edit from the Meta Information section in the left panel and start translating. In this case, I’ll translate the SEO page title.
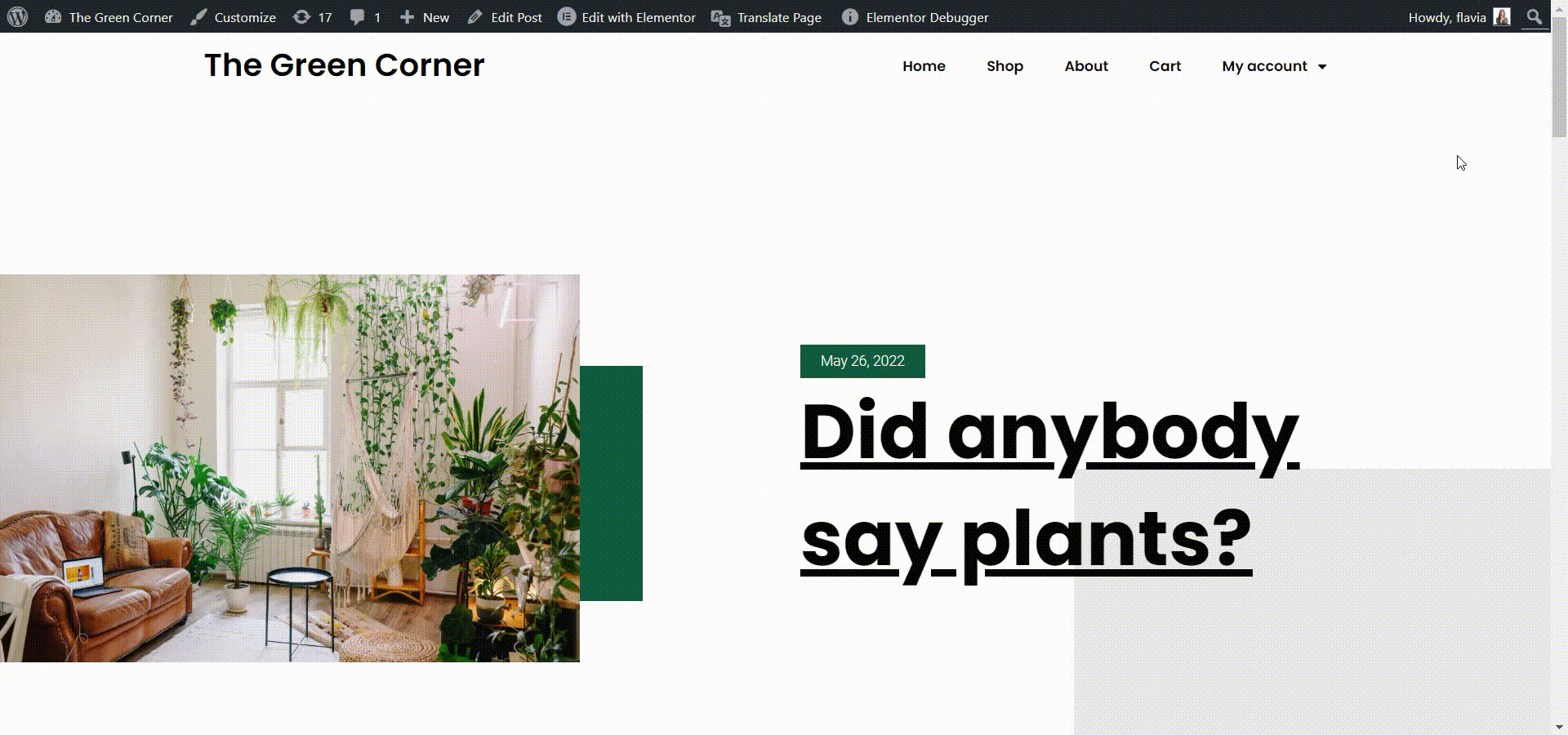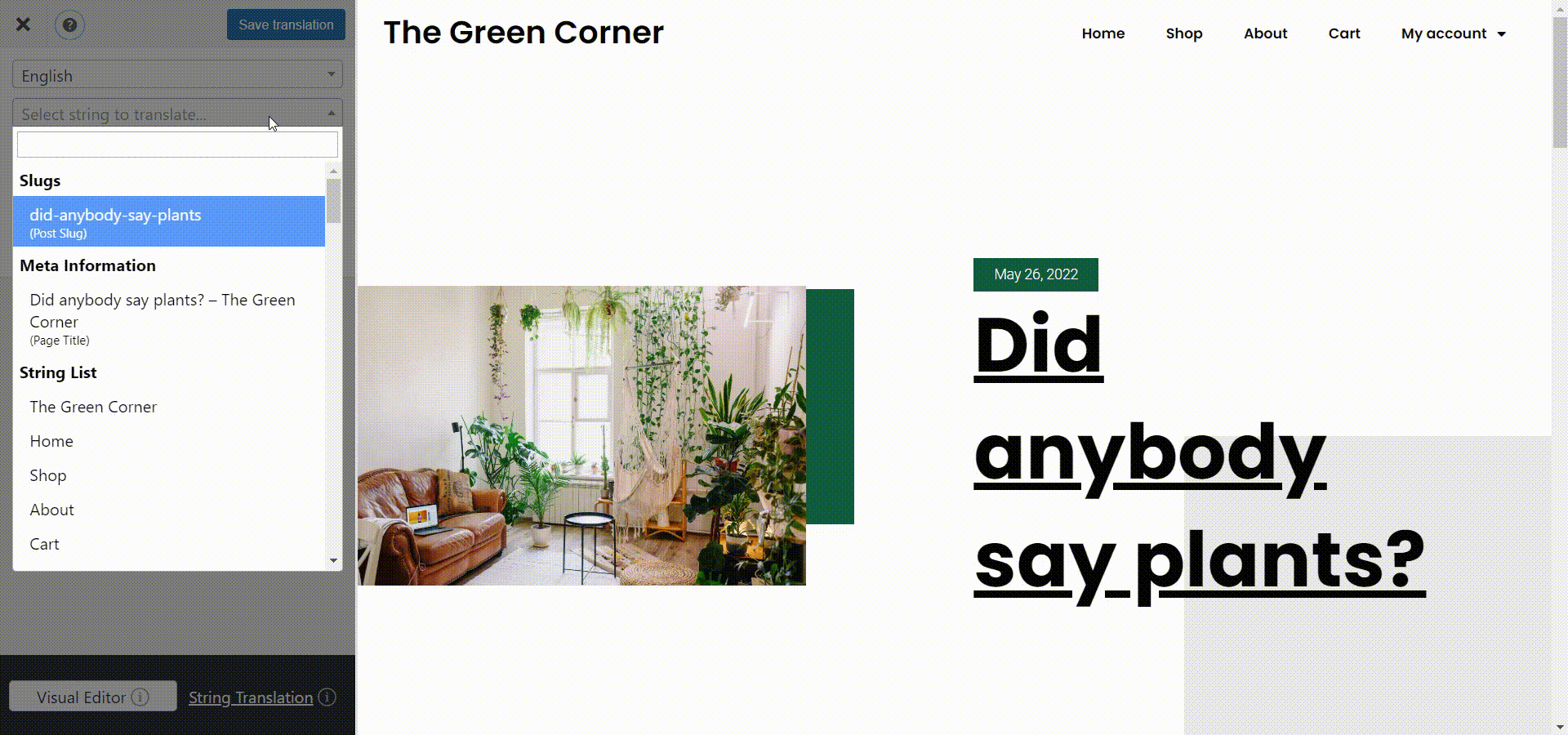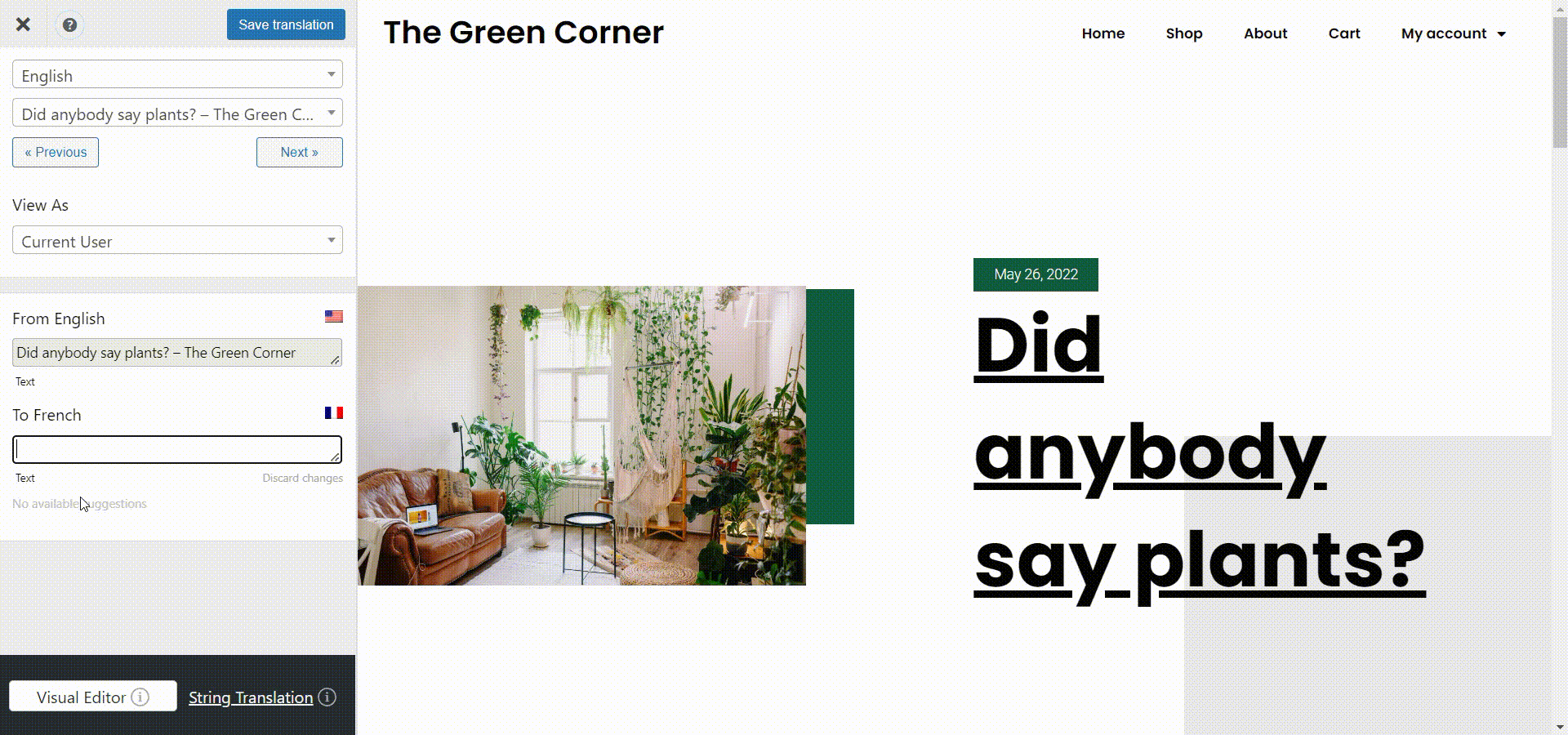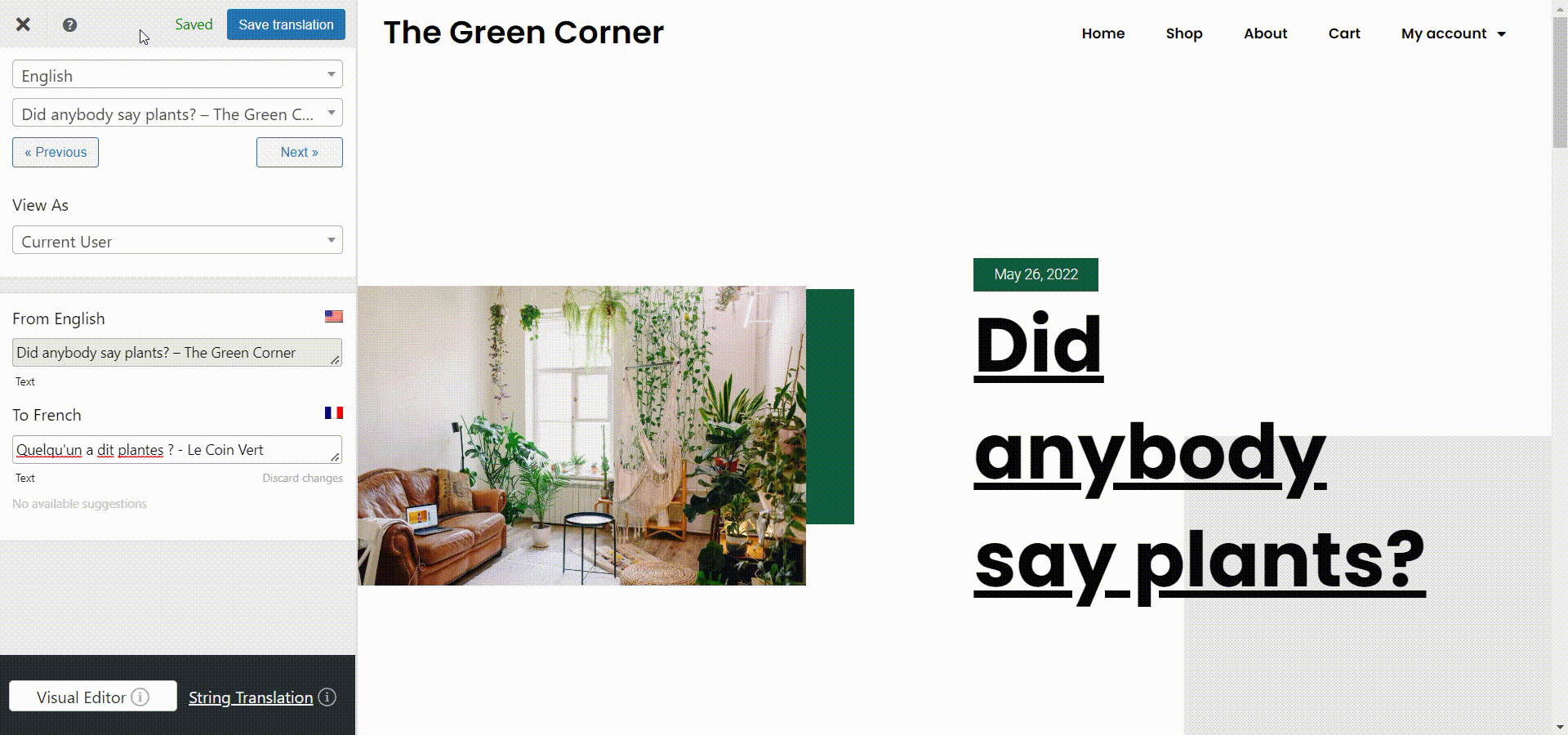
Once you’re done, click Save Translation and that’s it! You’ve translated your metadata.
7. Strategic Internal Linking
Internal linking, the practice of linking to other pages within the same website, is pivotal in SEO. It helps search engines understand your site’s structure, distributes page authority across your domain, and improves your site’s navigability for users.
When managing a multilingual website, it is crucial to ensure that internal links lead to the correct language version of a page. This practice enhances user experience and strengthens your site’s SEO performance by providing clear signals to search engines about the relationship between pages in different languages.
Multilingual SEO FAQs
Which CMS Is Best for Multilingual SEO?
WordPress is the arguably best CMS on the Internet for multilingual SEO. On its own, the software packs a lot of powerful easy-to-use features that make it easy to execute SEO for different languages effectively. When it comes to WordPress multilingual SEO, you can easily set things up with a plugin like TranslatePress. All you need to do is install the plugin, fill in the desired language and start translating.
What’s the Difference Between International SEO and Multilingual SEO?
Multilingual SEO involves the process of optimizing a website’s content for different audiences who speak various many languages. This is specifically important for businesses that want to reach a wider global audience.
In contrast, international SEO is content optimization for foreign countries but not necessarily those who speak other languages. For instance, a US-based business may want to reach a UK-based audience. What the business needs, in this case, is international SEO because of the varying versions of the English language and cultural context.
What Do You Need to Set up Multilingual SEO in WordPress?
- A robust translation plugin or service like TranslatePress
- A readable URL
- Properly researched keywords
- Hreflang tags
Driving Business Success with Multilingual SEO
Multilingual website SEO is no doubt an indispensable means of taking your business to a global level. Translating your website to one or more languages is a plus for your business, as it can help you grow multilingual traffic as well as increase conversions. But it’s not just enough to translate your website.
You need to apply langauge SEO best practices to take you a step further and connect you with the massive global audience you’ve always desired for your business.
The process may be tasking, but lucky for you, TranslatePress gives you an easy way out, making multilingual SEO a breeze.
TranslatePress Multilingual
TranslatePress is the easiest way to translate your WordPress site. It's fast, won't slow down your website, works with ANY theme or plugin and it's SEO friendly.
Get the pluginWe hope this article has helped you identify the key steps involved in executing multilingual website SEO effectively. Kindly let us know if you have any questions in the comments section below.
If you found this post helpful, please check out our YouTube channel, where we constantly upload short & easy-to-follow video tutorials. You can also follow us on Facebook and Twitter to be the first to know each time we post.


